Introduction :
Hypothyroidism, also known as an underactive thyroid, is a common yet often overlooked condition. It occurs when the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough hormones to meet the body's needs. While symptoms can develop slowly and be subtle, undiagnosed hypothyroidism can lead to significant health issues over time.
If you're constantly tired, gaining weight unexpectedly, or feeling cold even in warm weather, your thyroid might be the reason. Let’s explore the early warning signs of hypothyroidism, how to detect it, and what you can do about it.
What is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a thyroid disorder where the gland doesn’t produce sufficient levels of thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones regulate metabolism, energy, body temperature, and many other essential functions.
When hormone levels drop, body processes slow down, affecting multiple systems. Thyroid hormone deficiency impacts everything from digestion and skin to mental focus and reproductive health.
Most Common Causes of Hypothyroidism
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (autoimmune condition)
Thyroid surgery or radiation therapy
Iodine deficiency
Certain medications (e.g., lithium, amiodarone)
Congenital hypothyroidism in newborns
Pituitary gland dysfunction
Early Warning Signs of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism often presents subtle symptoms that people dismiss as stress, age, or lifestyle issues. However, if left untreated, the condition can worsen and affect overall well-being.
Here are the signs of underactive thyroid you might be missing:
1. Chronic Fatigue
Persistent tiredness and lack of energy, even after a full night’s sleep, is a common early symptom. If you're asking, "Why am I always tired?", it's worth checking your thyroid.
2. Unexplained Weight Gain
Slow metabolism due to low thyroid function can lead to gradual, unexplained weight gain, even if your diet hasn't changed.
3. Cold Sensitivity
Do you feel cold when everyone else is comfortable? Feeling cold all the time is linked to reduced metabolic activity caused by hypothyroidism.
4. Dry Skin and Hair
Low thyroid hormone levels reduce sweat and oil production, leading to dry, flaky skin, brittle nails, and hair thinning or hair loss.
5. Depression and Mood Changes
Hypothyroidism and depression are closely linked. You may experience low mood, anxiety, or irritability due to hormonal imbalance.
6. Brain Fog and Memory Issues
Forgetfulness, poor concentration, and mental sluggishness are often labeled as “just stress,” but they could signal thyroid-related cognitive dysfunction.
7. Constipation
Slower digestive function is a hallmark sign of low thyroid. If you’ve been struggling with chronic constipation, it might not just be your diet.
8. Irregular Periods or Fertility Problems
In women, thyroid imbalances can cause irregular menstrual cycles, heavier periods, or difficulty conceiving.
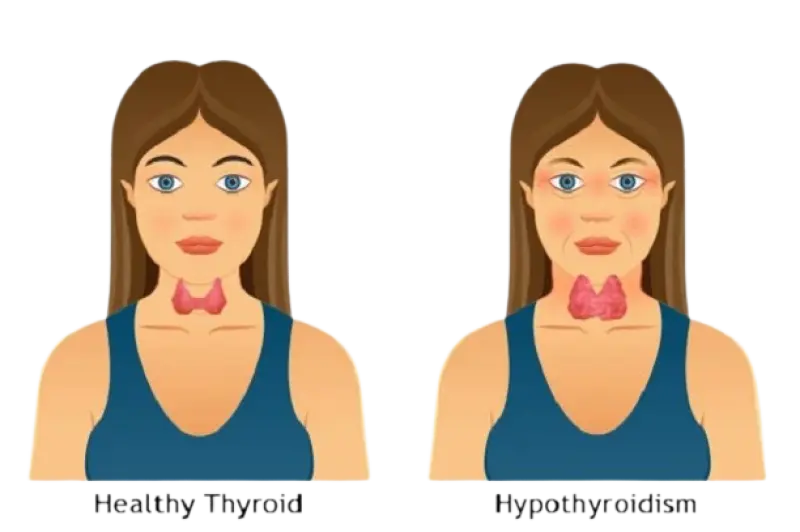
9. Swelling in the Neck (Goiter)
An enlarged thyroid gland can cause a visible swelling in the neck, signaling thyroid distress.
10. Low Heart Rate
A sluggish thyroid can reduce heart rate, causing fatigue, dizziness, or chest discomfort.
Who is at Risk for Hypothyroidism?
You are more likely to develop hypothyroidism if you:
Are a woman over 30
Have a family history of thyroid disorders
Have autoimmune diseases like Type 1 diabetes or lupus
Have had thyroid surgery or radiation
Are pregnant or postpartum
Hypothyroidism in Women
Women are up to 10 times more likely to develop hypothyroidism than men. It can severely affect fertility, pregnancy, and menstrual health.
Signs of hypothyroidism in females include:
Irregular or heavy periods
PCOS-like symptoms
Mood swings
Difficulty losing weight
Hair thinning and fatigue
Searching “hypothyroidism symptoms in females” is common because these symptoms often mimic other hormonal issues.
How is Hypothyroidism Diagnosed?
Your doctor may recommend blood tests such as:
TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
Free T4 and Free T3 levels
Thyroid antibodies (TPO, TG) for Hashimoto’s
Early diagnosis can help prevent complications like heart problems, infertility, and goiter.
Treatment Options for Hypothyroidism
The main treatment is daily thyroid hormone replacement therapy using levothyroxine. It helps normalize hormone levels, improving energy, metabolism, and mood.
Lifestyle tips for managing hypothyroidism:
Get enough iodine and selenium through your diet
Exercise regularly for metabolism support
Avoid soy and gluten if they trigger autoimmune flares
Monitor your thyroid levels annually
Hypothyroidism Diet Tips
Although no food can cure hypothyroidism, some dietary choices support thyroid health:
Foods to Eat:
Iodine-rich foods: seaweed, dairy, eggs
Selenium sources: Brazil nuts, tuna
Zinc-rich foods: shellfish, legumes
Antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables
Foods to Avoid:
Raw cruciferous vegetables in excess (cabbage, broccoli)
Soy products
Gluten (especially if Hashimoto’s is present)
Highly processed foods and sugar
Looking up “best diet for hypothyroidism” can help guide your nutrition decisions.
Frequently Missed Hypothyroidism Symptoms
Puffy face or hands
Slowed reflexes
Hoarseness
Thinning eyebrows (especially outer third)
Pale or yellowish skin tone
These subtle symptoms often get overlooked or attributed to aging or stress.
FAQs About Hypothyroidism
Q1: What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism?
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disorder, is the most frequent cause.Q2: Can hypothyroidism be cured?
It can be managed effectively with hormone replacement, but it is usually a lifelong condition.Q3: How do I know if I have hypothyroidism?
Persistent fatigue, cold sensitivity, weight gain, and a blood test showing high TSH levels are key indicators.Q4: What are the first signs of thyroid problems?
Fatigue, hair thinning, constipation, and weight gain are early signs.Q5: Is hypothyroidism serious?
If left untreated, it can lead to heart disease, infertility, goiter, and mental health issues.Conclusion: Don’t Miss the Signs of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is easy to overlook but important to detect. If you're experiencing tiredness, weight gain, or mood changes, talk to your doctor. Early diagnosis and proper treatment can restore energy, improve metabolism, and protect your long-term health.