Among these, EDTA tubes play a vital role in ensuring
reliable hematological results. At Aarogyaa Bharat, we believe that
understanding medical consumables empowers better healthcare decisions. This
blog offers a complete, easy-to-understand guide on EDTA tubes their definition,
history, types, and laboratory applications.
What Is an EDTA Tube?
An EDTA tube is a blood collection tube that contains Ethylene
Diamine Tetra Acetic Acid (EDTA) as an anticoagulant. EDTA works by binding
calcium ions in the blood, preventing clot formation. Since calcium is
essential for blood coagulation, removing it ensures the blood sample remains
in a liquid state.
These tubes are most commonly identified by their lavender
or purple coloured caps and are widely used in diagnostic laboratories for hematology
tests.
Brief History of EDTA Tubes
The use of anticoagulants in blood testing dates back to the
early 20th century when scientists realized that clotted samples led to
inaccurate results. EDTA was later introduced as a superior anticoagulant
because:
- It
preserved cell morphology better than heparin or citrate
- It
provided consistent results for cell counting
- It
was stable and effective even in small quantities
Over time, EDTA tubes became the gold standard for hematology
testing, revolutionizing complete blood count (CBC) analysis and advancing
diagnostic accuracy worldwide.
Why EDTA Is Important in Blood Testing
EDTA is preferred because it:
- Prevents
clotting without altering cell size
- Preserves
red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
- Minimizes
sample degradation during transport
- Ensures
accurate cell counts and morphology
Because of these benefits, EDTA tubes are indispensable in
both routine and specialized laboratory investigations.
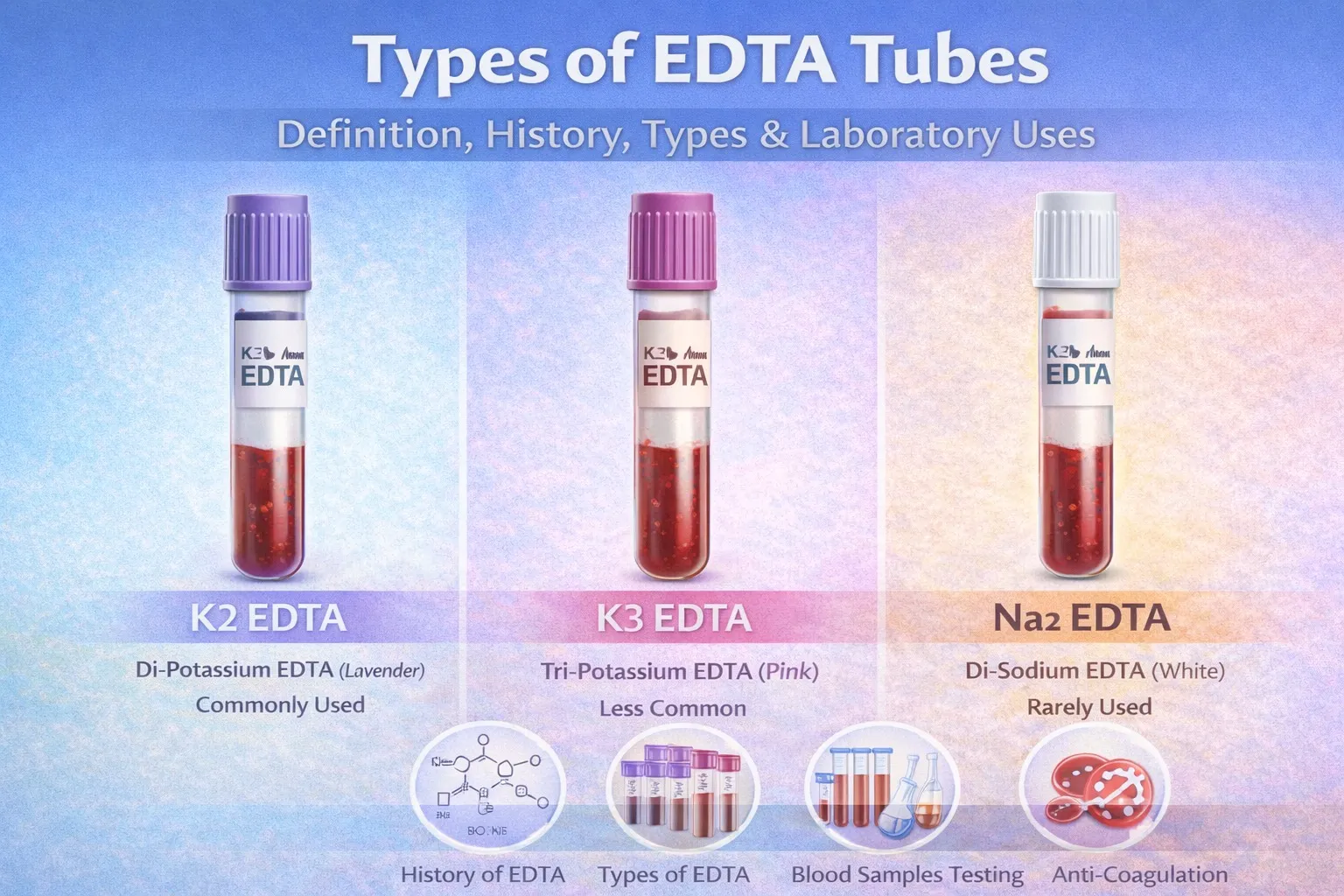
Types of EDTA Tubes
EDTA tubes are available in different formulations and
sizes, depending on laboratory requirements.
1. K2 EDTA Tubes
- Contains
spray-dried dipotassium EDTA
- Most
commonly used EDTA tube
- Ideal
for CBC, ESR, and blood grouping
- Minimal
dilution of blood sample
Best for: Routine hematology tests
2. K3 EDTA Tubes
- Contains
liquid Tri potassium EDTA
- Slightly
dilutes the blood sample
- Less
commonly used today
Best for: Older analyzers or specific protocols
3. Micro EDTA Tubes
- Designed
for pediatric and neonatal patients
- Requires
very small blood volume
- Often
used for capillary blood collection
Best for: Newborns and infants
4. Vacuum vs Non-Vacuum EDTA Tubes
- Vacuum
tubes: Ensure precise blood-to-anticoagulant ratio
- Non-vacuum
tubes: Used in manual collection settings
Common Laboratory Uses of EDTA Tubes
EDTA tubes are primarily used in hematology and blood
analysis, including:
- Complete
Blood Count (CBC)
- Hemoglobin
estimation
- Platelet
count
- Peripheral
blood smear
- Blood
grouping and cross-matching
- ESR
(Wintrobe method)
They are not suitable for calcium, potassium, or coagulation
studies, as EDTA interferes with these parameters.
Proper Handling and Storage of EDTA Tubes
To ensure accurate test results:
- Fill
the tube to the recommended level
- Gently
invert the tube 6–8 times after collection
- Avoid
shaking vigorously to prevent hemolysis
- Store
samples at recommended temperatures
- Process
samples within the stipulated time
At Aarogyaa Bharat, we emphasize best practices to maintain
sample integrity and patient safety.
Advantages of Using EDTA Tubes
- High
accuracy in hematology results
- Excellent
preservation of cell structure
- Reduced
risk of clot formation
- Compatible
with automated analyzers
- Widely
available and cost-effective
Limitations of EDTA Tubes
- Cannot
be used for coagulation tests
- Interferes
with calcium and potassium measurements
- Overfilling
or underfilling can affect results
Understanding these limitations helps laboratories choose
the right tube for the right test.
Role of EDTA Tubes in Modern Diagnostics
From small pathology labs to large hospital diagnostic centers,
EDTA tubes remain a backbone of blood testing. With increasing reliance on
automated analyzers and precision diagnostics, the demand for high-quality EDTA
tubes continues to grow.
At Aarogyaa Bharat, we support healthcare providers with reliable medical consumables that meet clinical and laboratory standards.
Conclusion
EDTA tubes may appear simple, but their role in accurate
diagnosis is critical. From preserving blood cells to enabling precise hematology
analysis, they form the foundation of countless medical decisions every day. By
understanding their types, uses, and limitations, healthcare professionals can
ensure better patient outcomes.
Aarogyaa Bharat remains committed to delivering trusted
medical knowledge and quality healthcare solutions for laboratories, hospitals,
and caregivers across India.