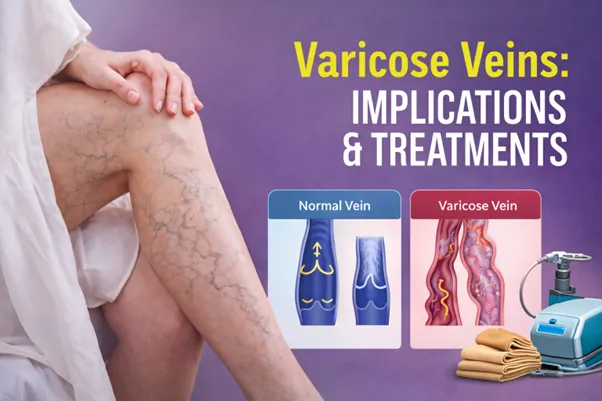
While varicose veins are sometimes dismissed as a cosmetic
issue, they can cause significant discomfort, pain, and medical complications
if left untreated. Understanding their causes, implications, and available
treatments is essential for timely care and long-term leg health.
What Are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins occur when the valves inside veins stop
functioning properly. Normally, these valves ensure that blood flows in one
direction back toward the heart. When the valves weaken or fail, blood begins
to pool inside the veins, causing them to stretch, enlarge, and become twisted.
This condition most commonly affects the legs, as gravity
makes it harder for blood to return to the heart from the lower extremities.
Why Are Varicose Veins More Common in Women?
Women are more prone to varicose veins due to:
- Hormonal
changes during pregnancy, menopause, or menstruation
- Use
of oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy
- Increased
pressure on leg veins during pregnancy
- Genetic
predisposition
However, men can also develop varicose veins, especially
with advancing age or lifestyle risk factors.
Common Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Symptoms can range from mild to severe and often worsen
after prolonged standing.
Early Symptoms
- Visible,
bulging veins
- Mild
leg heaviness or fatigue
- Occasional
aching
Progressive Symptoms
- Persistent
leg pain or burning sensation
- Swelling
in ankles and feet
- Itching
around affected veins
- Muscle
cramps, especially at night
- Skin
discoloration or dryness
Medical Implications of Untreated Varicose Veins
Ignoring varicose veins can lead to serious complications,
including:
1. Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Poor blood circulation can result in long-term swelling,
skin damage, and discomfort.
2. Skin Changes and Ulcers
Prolonged venous pressure can cause:
- Darkening
of skin
- Hardening
of tissues
- Painful
leg ulcers near the ankles
3. Blood Clots
In rare cases, varicose veins may lead to superficial
thrombophlebitis or deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
4. Bleeding
Enlarged veins close to the skin surface may rupture even
with minor injury.
What Causes Varicose Veins?
Several factors increase the risk:
- Prolonged
standing or sitting
- Obesity
- Lack
of physical activity
- Aging
- Family
history
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
Lifestyle plays a significant role in both development and
progression.
How Are Varicose Veins Diagnosed?
Doctors typically diagnose varicose veins through:
- Physical
examination
- Medical
history assessment
- Doppler
ultrasound to evaluate blood flow and valve function
Early diagnosis allows for simpler and more effective
treatment.
Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
Treatment depends on severity, symptoms, and patient
preference.
1. Lifestyle and Home-Based Management
Mild cases may improve with:
- Regular
exercise
- Weight
management
- Elevating
legs
- Avoiding
prolonged standing
- Wearing
compression stockings
These measures help improve circulation and reduce symptoms.
2. Compression Therapy
Medical-grade compression stockings apply controlled
pressure to the legs, helping veins move blood more efficiently.
3. Sclerotherapy
A minimally invasive procedure where a solution is injected
into affected veins, causing them to collapse and fade over time.
4. Laser or Radiofrequency Treatment
Advanced procedures that use heat energy to close off
damaged veins. These are:
- Minimally
invasive
- Performed
on an outpatient basis
- Associated
with quick recovery
5. Surgical Options
In severe cases, vein ligation or stripping may be
recommended, though modern minimally invasive techniques are now preferred.
Prevention Tips for Varicose Veins
While not all cases are preventable, risk can be reduced by:
- Staying
physically active
- Avoiding
long periods of immobility
- Maintaining
a healthy weight
- Wearing
comfortable footwear
- Elevating
legs regularly
Early lifestyle changes can slow disease progression.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Are varicose veins dangerous?
They are usually not life-threatening but can cause
complications if untreated.
Q2. Can varicose veins go away on their own?
No. They may worsen over time without treatment, though
symptoms can be managed.
Q3. Is treatment painful?
Most modern treatments are minimally invasive and involve
little discomfort.
Q4. Can young people get varicose veins?
Yes, especially if there is a genetic predisposition or lifestyle risk factors.
Living Comfortably with Varicose Veins
With timely diagnosis and proper treatment, people with
varicose veins can:
- Reduce
pain and swelling
- Improve
mobility
- Prevent
complications
- Enhance
quality of life
Modern medical advances have made treatment safer, faster,
and more accessible than ever.
Conclusion
Varicose veins are more than just a cosmetic concern. They
are a sign of underlying venous dysfunction that can lead to discomfort and
serious complications if ignored. Understanding the implications and seeking
appropriate treatment can prevent long-term problems.
Early medical advice, lifestyle modifications, and modern
treatment options allow individuals to manage varicose veins effectively and
maintain healthy, active legs.