This procedure is commonly performed during surgery,
emergency care, critical illness, and respiratory failure.
At AarogyaaBharat.com, we aim to explain essential medical
procedures in a clear, patient-friendly, and clinically accurate way.
What Is Intubation?
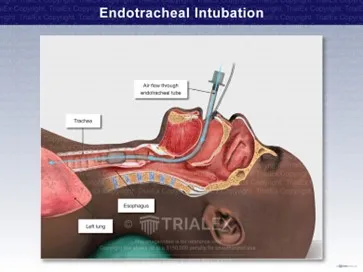
Intubation (pronounced in-too-BEY-shuhn) is the process of
placing an endotracheal tube into the airway to:
- Maintain
a clear airway
- Support
breathing
- Protect
the lungs from aspiration
Once the tube is in place, breathing may be assisted or
fully controlled using a ventilator or manual resuscitation bag.
Why Is Endotracheal Intubation Needed?
Endotracheal intubation is performed when a person cannot
breathe adequately on their own or when airway protection is required.
Common Indications
- General
anesthesia during surgery
- Severe
respiratory distress or failure
- Cardiac
arrest
- Trauma
or head injury
- Severe
infections affecting breathing
- Airway
obstruction or swelling
- Reduced
consciousness (coma)
How Is Endotracheal Intubation Performed?
The procedure is carried out by trained professionals such
as anesthesiologists, emergency physicians, or critical care specialists.
Step-by-Step Overview
- The
patient is positioned properly
- Sedation
or anesthesia is given (in most cases)
- A
laryngoscope is used to visualize the vocal cords
- The
endotracheal tube is passed into the trachea
- The
tube cuff is inflated to secure the airway
- Placement is confirmed using:
- Chest movement
- Breath sounds
- Capnography
- Chest X-ray
Types of Endotracheal Intubation
1. Oral Intubation
- Tube
inserted through the mouth
- Most
common method
- Used
in emergency and surgical settings
2. Nasal Intubation
- Tube
inserted through the nose
- Used
in selected surgical cases or limited mouth opening
Risks and Possible Complications
Although intubation is life-saving, it can have risks,
especially in emergency situations.
Possible Complications
- Sore
throat or hoarseness
- Dental
or lip injury
- Incorrect
tube placement
- Tracheal
irritation
- Lung
infection (ventilator-associated pneumonia)
Proper technique and monitoring significantly reduce these
risks.
Endotracheal Intubation vs Tracheostomy
|
Feature |
Endotracheal
Intubation |
Tracheostomy |
|
Duration |
Short-term |
Long-term |
|
Entry |
Mouth or nose |
Surgical neck
opening |
|
Comfort |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Speech |
Not possible |
Possible with
devices |
Patient Care After Intubation
Post-intubation care includes:
- Continuous
monitoring of oxygen levels
- Regular
suctioning of secretions
- Maintaining
proper tube position
- Oral
hygiene to prevent infection
- Monitoring
cuff pressure
How Aarogyaa Bharat Supports Airway Management
At Aarogyaa Bharat, we support healthcare providers and
patients by offering:
- Quality
airway management products
- Endotracheal
tubes and critical care equipment
- Educational
medical content
- Trusted healthcare solutions for hospitals and home care
Conclusion
Endotracheal intubation is a critical medical procedure that
saves lives by securing the airway and supporting breathing. It is widely used
in surgery, emergencies, and intensive care settings. Understanding the
procedure, indications, and care helps patients and caregivers feel more
informed and confident.
For trusted medical education and equipment insights,
Aarogyaa Bharat remains your reliable healthcare partner.