A Complete Home-Care Guide to Monitoring Blood Oxygen
Levels and Heart Health
During the COVID-19 pandemic, pulse oximeters became
household essentials almost overnight. Families across India rushed to buy them
to track falling oxygen levels and detect silent hypoxia early. Even after the
pandemic, the importance of pulse oximeters has not faded. Doctors now
routinely recommend pulse oximeters for patients with respiratory problems,
heart disease, elderly individuals, athletes, and people recovering from
infections or surgery.
Despite their widespread use, many people still do not fully
understand what a pulse oximeter actually measures, how accurate it is, when it
should be used, and why it truly matters for long-term health. Some users panic
over small fluctuations in readings, while others ignore dangerously low values
due to lack of awareness. This confusion can lead to unnecessary anxiety,
delayed treatment, or even life-threatening situations.
At Aarogyaa Bharat - Live Healthy, Live Better, we regularly
guide families on choosing and using pulse oximeters correctly as part of
complete home-care monitoring. In this in-depth guide, you will learn what a
pulse oximeter is, what it measures, how it works, why it matters, who should
use it, how to interpret readings, how to choose the best pulse oximeter in
India, common mistakes to avoid, and how it can save lives through early
detection.
What Is a Pulse Oximeter?
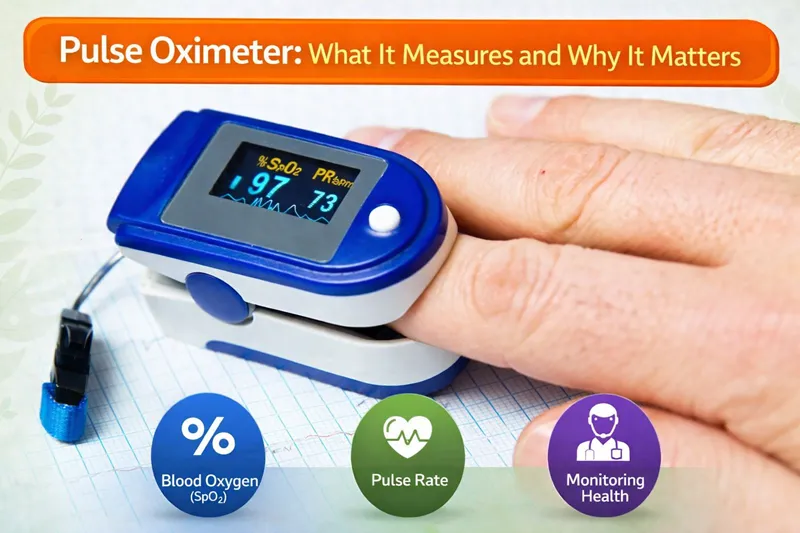
A pulse oximeter is a small, non-invasive medical device
that measures the oxygen saturation level (SpO₂) in your blood and your pulse
rate. It is usually clipped onto a fingertip, toe, or earlobe and provides
instant digital readings within a few seconds. This painless test does not
require blood samples or needles, making it ideal for frequent home use.
Pulse oximeters are widely used in hospitals, clinics,
ambulances, and now in millions of homes across India. They are especially
valuable for monitoring patients with respiratory conditions, heart diseases,
COVID-19 recovery, asthma, COPD, pneumonia, sleep apnea, and post-surgical
recovery. Many athletes also use pulse oximeters to track oxygen levels during
training and high-altitude activities.
What makes pulse oximeters so popular is their simplicity
and affordability. Even basic models provide reliable oxygen saturation and
pulse rate readings, making them accessible to almost every household. Advanced
models may also include features such as perfusion index, plethysmograph
waveform, alarm alerts, and Bluetooth connectivity.
Understanding what a pulse oximeter is and what it does is
the first step toward using it effectively for long-term health monitoring.
What Does a Pulse Oximeter Measure?
A pulse oximeter primarily measures two vital health
parameters:
- Oxygen
Saturation (SpO₂)
- Pulse
Rate (Heart Rate)
Oxygen saturation refers to the percentage of haemoglobin in
your blood that is carrying oxygen. Haemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells
responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. A
healthy oxygen saturation level ensures that all organs and tissues receive
sufficient oxygen to function properly.
Pulse rate, also known as heart rate, indicates the number
of times your heart beats per minute. Monitoring pulse rate helps assess
cardiovascular health, detect irregular heart rhythms, and evaluate physical
fitness.
Some advanced pulse oximeters also measure additional
parameters such as:
- Perfusion
Index (PI) - Indicates blood flow strength at the measurement site
- Respiratory
Rate (RR) - Estimates breathing rate
- Plethysmograph
Waveform - Visual representation of pulse strength
These extra features provide deeper insights into a
patient’s circulatory and respiratory health, especially in critical care and
long-term monitoring scenarios.
What Is Oxygen Saturation (SpO₂) and Why Is It Important?
Oxygen saturation (SpO₂) is one of the most important
indicators of respiratory health. It shows how efficiently oxygen is being
transported from your lungs into your bloodstream and delivered to vital
organs.
A normal SpO₂ level for healthy adults typically ranges
between 95% and 100%. Values below this range may indicate breathing problems,
lung disease, heart issues, or poor oxygen delivery to tissues. When oxygen
saturation falls too low, the body’s organs including the brain, heart, and
kidneys can suffer serious damage.
Low oxygen levels, a condition known as hypoxemia, can cause
symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, confusion, dizziness,
fatigue, bluish lips or fingertips, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness.
However, in some patients, oxygen levels may drop silently without obvious
symptoms, a phenomenon known as silent hypoxia.
This is why monitoring SpO₂ using a pulse oximeter is so
important. Early detection of falling oxygen levels allows timely medical
intervention, which can prevent complications, hospitalizations, and even
death.
What Is a Normal Pulse Oximeter Reading?
Understanding what is considered a normal reading helps
users interpret their pulse oximeter results accurately.
|
SpO₂ Level |
Meaning |
|
95% - 100% |
Normal oxygen
level |
|
90% - 94% |
Mild
hypoxemia (monitor closely) |
|
85% - 89% |
Moderate
hypoxemia (medical attention needed) |
|
Below 85% |
Severe
hypoxemia (emergency) |
For pulse rate, normal values vary depending on age, fitness
level, and health condition.
|
Age Group |
Normal
Pulse Rate (BPM) |
|
Infants |
100 - 160 |
|
Children |
70 - 120 |
|
Adults |
60 - 100 |
|
Athletes |
40 - 60 |
It is important to remember that individual baselines may
vary. Some COPD patients may have a stable SpO₂ around 90-92% under medical
supervision. Always consult your doctor to determine what is normal for your
specific condition.
How Does a Pulse Oximeter Work?
Pulse oximeters use a technology called photoplethysmography
to measure oxygen saturation. The device emits two different wavelengths of
light red and infrared through your fingertip or earlobe. These light beams
pass through your blood and are partially absorbed by oxygenated and
deoxygenated haemoglobin.
The device’s sensor detects how much light is absorbed at
each wavelength and calculates the ratio between oxygenated and deoxygenated
blood. Based on this data, the pulse oximeter estimates your SpO₂ level and
displays it digitally on the screen.
Pulse rate is measured by detecting tiny changes in blood
volume that occur with each heartbeat. These changes are captured by the light
sensor and converted into a pulse waveform, which is then translated into beats
per minute (BPM).
This entire process happens in seconds, making pulse
oximeters incredibly fast, convenient, and non-invasive for real-time health
monitoring.
Why Does a Pulse Oximeter Matter So Much?
A pulse oximeter matters because it provides early warning
signs of respiratory and cardiovascular problems before they become
life-threatening. Many serious conditions, including COVID-19, pneumonia,
asthma attacks, COPD flare-ups, heart failure, and sleep apnea, can cause
oxygen levels to drop silently.
Without a pulse oximeter, patients may not realize their
oxygen levels are dangerously low until severe symptoms appear. By that time,
emergency hospitalization may be required. A pulse oximeter allows patients and
caregivers to monitor oxygen levels regularly and seek medical help at the
right time.
Pulse oximeters are also invaluable for monitoring recovery
progress after respiratory infections, surgeries, and hospital discharge. They
help doctors assess whether home oxygen therapy or medication adjustments are
needed.
For elderly individuals and high-risk patients, keeping a
pulse oximeter at home offers peace of mind and improves overall health
management. It empowers families to take proactive control of their health
rather than reacting to emergencies.
Who Should Use a Pulse Oximeter?
Pulse oximeters are beneficial for a wide range of people,
not just those with serious illnesses. Asthma and COPD patients use them to
monitor breathing efficiency and detect early flare-ups. COVID-19 and
post-COVID patients rely on pulse oximeters to track oxygen recovery and
identify complications.
Heart patients use pulse oximeters to monitor circulation
efficiency and detect worsening heart failure. Elderly individuals benefit from
regular monitoring due to age-related decline in lung and heart function.
Sleep apnea patients use pulse oximeters to detect night-time
oxygen drops. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts monitor oxygen levels during
intense training and high-altitude activities.
Smokers and people exposed to air pollution also benefit
from periodic oxygen monitoring to assess long-term lung health.
Pulse Oximeter vs Blood Oxygen Test: What’s the
Difference?
|
Feature |
Pulse
Oximeter |
Blood
Oxygen Test (ABG) |
|
Invasiveness |
Non-invasive |
Invasive
(blood draw) |
|
Speed |
Instant |
Lab
processing required |
|
Cost |
Low |
High |
|
Accuracy |
High for
trends |
Very high
(gold standard) |
|
Usage |
Home
monitoring |
Hospital
diagnosis |
Pulse oximeters are ideal for continuous home monitoring,
while blood oxygen tests are used in hospitals for precise diagnostic
confirmation.
How to Use a Pulse Oximeter Correctly
Using a pulse oximeter correctly ensures accurate readings.
Start by sitting calmly and resting for at least 5 minutes before measurement.
Remove nail polish, artificial nails, or henna, as these can interfere with
light transmission.
Place the device on a clean, warm fingertip and keep your
hand still at heart level. Avoid talking or moving during measurement. Wait for
the reading to stabilize before recording it.
Take multiple readings at different times of the day to
identify trends rather than relying on a single value. If readings are
consistently low or fluctuate significantly, consult a doctor immediately.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using a Pulse Oximeter
Many users panic over minor fluctuations or take readings
immediately after physical activity, which can lead to inaccurate results. Cold
fingers, poor circulation, nail polish, and bright ambient light can also
affect readings.
Relying on a single low reading without rechecking can cause
unnecessary anxiety. Always take 2-3 readings and look for consistent patterns.
Using cheap, unbranded pulse oximeters with poor sensors can
result in unreliable data. Always choose certified medical devices from trusted
brands.
How to Choose the Best Pulse Oximeter in India
When choosing a pulse oximeter, focus on accuracy, display
quality, battery life, and certification. Look for models with bright OLED
displays, low battery indicators, and automatic shut-off features.
Advanced features such as plethysmograph waveform, alarm
alerts, and Bluetooth connectivity are useful for long-term monitoring. Always
choose a medically certified device with warranty coverage and after-sales
support.
At Aarogyaa Bharat, we offer certified pulse oximeters with
expert guidance to ensure safe and reliable home health monitoring.
Conclusion
A pulse oximeter is not just a gadget it is a life-saving health monitoring
tool that every household should own. It provides early detection of oxygen
level drops, helps monitor chronic respiratory conditions, and supports safe
recovery after illness or surgery.
At Aarogyaa Bharat - Live Healthy, Live Better, we believe
that proactive health monitoring saves lives. Our goal is to help families
choose the safest and most reliable pulse oximeters for long-term home care.